We published a new paper “Auditing for Discrimination in Algorithms Delivering Job Ads” (updated 2025: link was https://ant.isi.edu/~imana/papers/Imana2021a.pdf) by Basileal Imana (University of Southern California), Aleksandra Korolova (University of Southern California) and John Heidemann (University of Southern California/ISI) at TheWebConf 2021 (WWW ’21).
From the abstract:
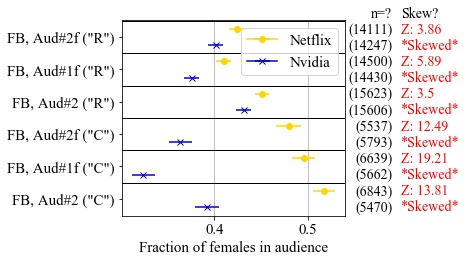
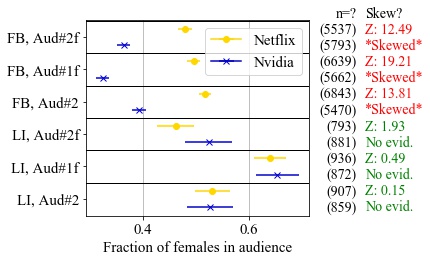
Ad platforms such as Facebook, Google and LinkedIn promise value for advertisers through their targeted advertising. However, multiple studies have shown that ad delivery on such platforms can be skewed by gender or race due to hidden algorithmic optimization by the platforms, even when not requested by the advertisers. Building on prior work measuring skew in ad delivery, we develop a new methodology for black-box auditing of algorithms for discrimination in the delivery of job advertisements. Our first contribution is to identify the distinction between skew in ad delivery due to protected categories such as gender or race, from skew due to differences in qualification among people in the targeted audience. This distinction is important in U.S. law, where ads may be targeted based on qualifications, but not on protected categories. Second, we develop an auditing methodology that distinguishes between skew explainable by differences in qualifications from other factors, such as the ad platform’s optimization for engagement or training its algorithms on biased data. Our method controls for job qualification by comparing ad delivery of two concurrent ads for similar jobs, but for a pair of companies with different de facto gender distributions of employees. We describe the careful statistical tests that establish evidence of non-qualification skew in the results. Third, we apply our proposed methodology to two prominent targeted advertising platforms for job ads: Facebook and LinkedIn. We confirm skew by gender in ad delivery on Facebook, and show that it cannot be justified by differences in qualifications. We fail to find skew in ad delivery on LinkedIn. Finally, we suggest improvements to ad platform practices that could make external auditing of their algorithms in the public interest more feasible and accurate.
This paper was awarded runner-up for best student paper at The Web Conference 2021.
The data from this paper is upon request, please see our dataset page.
This work was reported in the popular press: The Intercept, MIT Technology Review, Wall Street Journal, The Register, VentureBeat, Reuters, The Verge, Engadget, Associated Press.