Basileal Imana presented the paper “Enumerating Privacy Leaks in DNS Data Collected above the Recursive” at NDSS DNS Privacy Workshop in San Diego, California, USA on February 18, 2018. Talk slides are available at https://ant.isi.edu/~imana/presentations/Imana18b.pdf and paper is available at https://ant.isi.edu/~imana/papers/Imana18a.pdf, or can be found at the DNS privacy workshop page.
From the abstract:
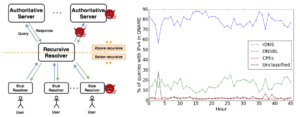
As with any information system consisting of data derived from people’s actions, DNS data is vulnerable to privacy risks. In DNS, users make queries through recursive resolvers to authoritative servers. Data collected below (or in) the recursive resolver directly exposes users, so most prior DNS data sharing focuses on queries above the recursive resolver. Data collected above a recursive resolver has largely been seen as posing a minimal privacy risk since recursive resolvers typically aggregate traffic for many users, thereby hiding their identity and mixing their traffic. Although this assumption is widely made, to our knowledge it has not been verified. In this paper we re-examine this assumption for DNS traffic above the recursive resolver. First, we show that two kinds of information appear in query names above the recursive resolver: IP addresses and sensitive domain names, such as those pertaining to health, politics, or personal or lifestyle information. Second, we examine how often these classes of potentially sensitive names appear in Root DNS traffic, using 48 hours of B-Root data from April 2017.
This is a joint work by Basileal Imana (USC), Aleksandra Korolova (USC) and John Heidemann (USC/ISI).
The DITL dataset (ITL_B_Root-20170411) used in this work is available from DHS IMPACT, the ANT project, and through DNS-OARC.