Wes Hardaker gave the talk “Verfploeter: Broad and Load-Aware Anycast Mapping” at DNS-OARC in San Jose, California, USA on September 29, 2017. Slides are available at on the event page.
From the abstract:
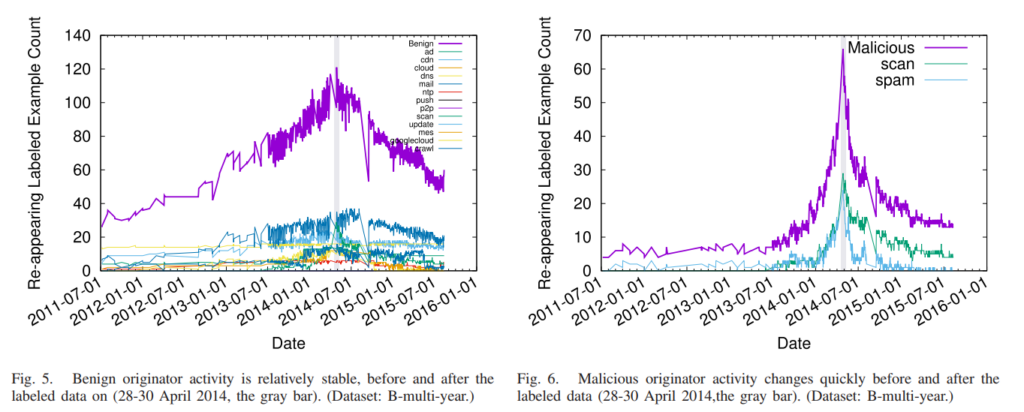
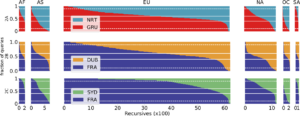
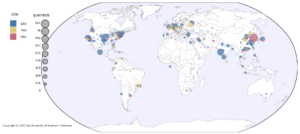
IP anycast provides DNS operators and CDNs with automatic fail-over and reduced latency by breaking the Internet into catchments,each served by a different anycast site. Unfortunately, understanding and predicting changes to catchments as sites are added or removed has been challenging. Current tools such as RIPE Atlas or commercial equivalents map from thousands of vantage points (VPs),but their coverage can be inconsistent around the globe. This paper proposes Verfploeter, a new method that maps anycast catchments using active probing. Verfploeter provides around 3.8M virtual VPs, 430 times the 9k physical VPs in RIPE Atlas,providing coverage of the vast majority of networks around the globe. We then add load information from prior service logs to provide calibrated predictions of anycast changes. Verfploeter has been used to evaluate the new anycast for B-Root, and we also report its use of a nine-site anycast testbed. We show that the greater coverage made possible by Verfploeter’s active probing is necessary to see routing differences in regions that have sparse coverage from RIPE Atlas, like South America and China.
A video of the talk is available On YouTube.