On March 29, 2022 the paper “Old but Gold: Prospecting TCP to Engineer and Live Monitor DNS Anycast” by Giovane C. M. Moura, John Heidemann, Wes Hardaker, Pithayuth Charnsethikul, Jeroen Bulten, João M. Ceron, and Cristian Hesselman appeared that the 2022 Passive and Active Measurement Conference. We’re happy that it was awarded Best Paper for this year’s conference!
From the abstract:
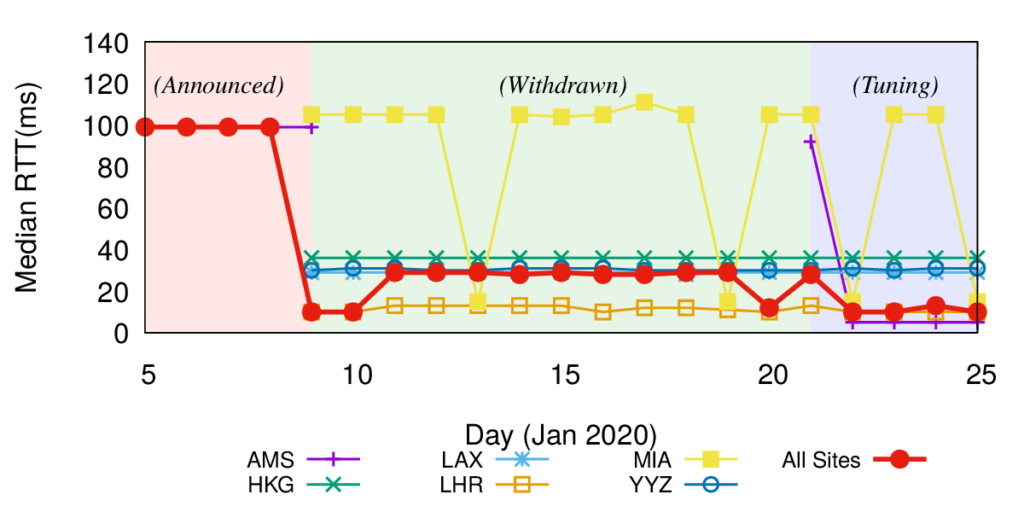
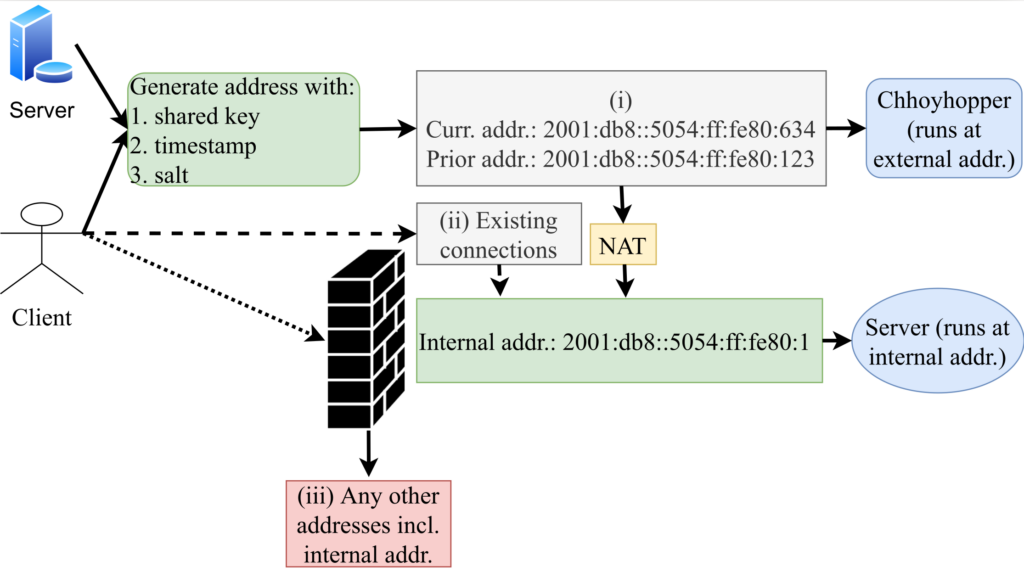
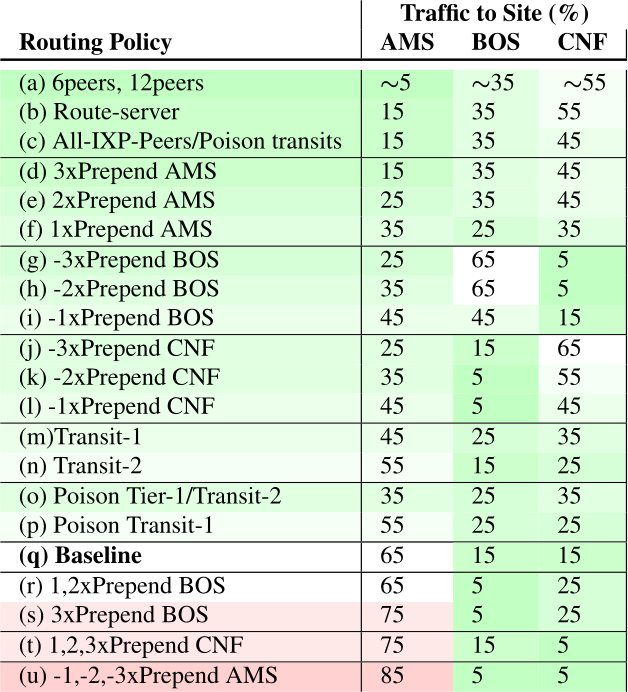
DNS latency is a concern for many service operators: CDNs exist to reduce service latency to end-users but must rely on global DNS for reachability and load-balancing. Today, DNS latency is monitored by active probing from distributed platforms like RIPE Atlas, with Verfploeter, or with commercial services. While Atlas coverage is wide, its 10k sites see only a fraction of the Internet. In this paper we show that passive observation of TCP handshakes can measure live DNS latency, continuously, providing good coverage of current clients of the service. Estimating RTT from TCP is an old idea, but its application to DNS has not previously been studied carefully. We show that there is sufficient TCP DNS traffic today to provide good operational coverage (particularly of IPv6), and very good temporal coverage (better than existing approaches), enabling near-real time evaluation of DNS latency from real clients. We also show that DNS servers can optionally solicit TCP to broaden coverage. We quantify coverage and show that estimates of DNS latency from TCP is consistent with UDP latency. Our approach finds previously unknown, real problems: DNS polarization is a new problem where a hypergiant sends global traffic to one anycast site rather than taking advantage of the global anycast deployment. Correcting polarization in Google DNS cut its latency from 100ms to 10ms; and from Microsoft Azure cut latency from 90ms to 20ms. We also show other instances of routing problems that add 100-200ms latency. Finally, real-time use of our approach for a European country-level domain has helped detect and correct a BGP routing misconfiguration that detoured European traffic to Australia. We have integrated our approach into several open source tools: Entrada, our open source data warehouse for DNS, a monitoring tool (ANTS), which has been operational for the last 2 years on a country-level top-level domain, and a DNS anonymization tool in use at a root server since March 2021.
The tools we developed in this paper are freely available, including patches to Knot, improvements to dnsanon, improvements to ENTRADA, and the new tool Anteater. Unfortunately data from the paper was from operational DNS systems and so cannot be shared due to privacy concerns.
This paper was made in part through DHS HSARPA Cyber Security Division via contract number HSHQDC-17-R-B0004-TTA.02-0006-I (PAADDOS) and by NWO, NSF CNS-1925737 (DIINER), and the Conconrdia Project, an European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program under Grant Agreement No 830927.