I would like to congratulate Dr. ASM Rizvi for defending his PhD at the University of Southern California in June 2024 and completing his doctoral dissertation “Mitigating Attacks that Disrupt Online Services Without Changing Existing Protocols”.
From the dissertation abstract:
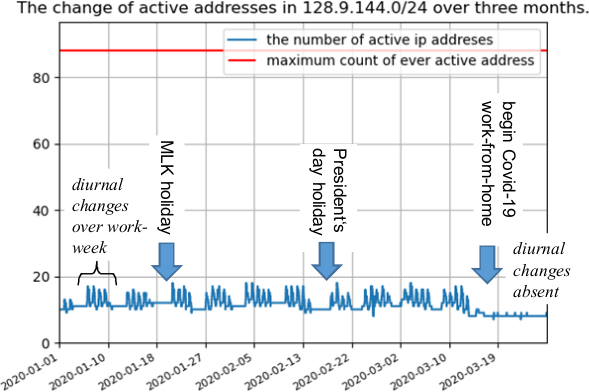
Service disruption is undesirable in today’s Internet connectivity due to its impacts on enterprise profits, reputation, and user satisfaction. We describe service disruption as any targeted interruptions caused by malicious parties in the regular user-to-service interactions and functionalities that affect service performance and user experience. In this thesis, we propose new methods that tackle service disruptive attacks using measurement without changing existing Internet protocols. Although our methods do not guarantee defense against all the attack types, our example defense systems prove that our methods generally work to handle diverse attacks. To validate our thesis, we demonstrate defense systems against three disruptive attack types. First, we mitigate Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks that target an online service. Second, we handle brute-force password attacks that target the users of a service. Third, we detect malicious routing detours to secure the path from the users to the server. We provide the first public description of DDoS defenses based on anycast and filtering for the network operators. Then, we show the first moving target defense utilizing IPv6 to defeat password attacks. We also demonstrate how regular observation of latency helps cellular users, carriers, and national agencies to find malicious routing detours. As a supplemental outcome, we show the effectiveness of measurements in finding performance issues and ways to improve using existing protocols. These examples show that our idea applies to different network parts, even if we may not mitigate all the attack types.
Rizvi’s PhD work was supported by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s HSARPA Cyber Security Division (HSHQDC-17-R-B0004-TTA.02-0006-I, PAADDOS) in a joint project with the Netherlands Organisation for scientific research (4019020199), the U.S. National Science Foundation (grant NSF OAC-1739034, DDIDD; CNS-2319409, PIMAWAT; CRI-8115780, CLASSNET; CNS-1925737, DIINER ) and U.S. DARPA (HR001120C0157, SABRES), and Akamai.
Most data from his papers is available at no cost from ANT; please see specific publications for details.