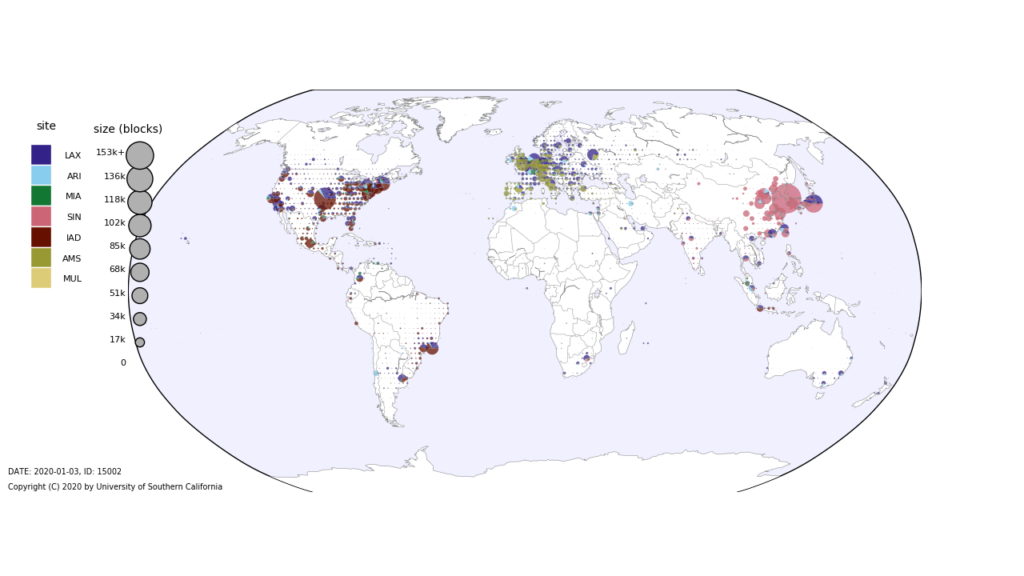
Our new paper “Anycast Polarization in The Wild” will appear at the 2024 Conference on Passive and Active Measurements (PAM 2024).
From the abstract:
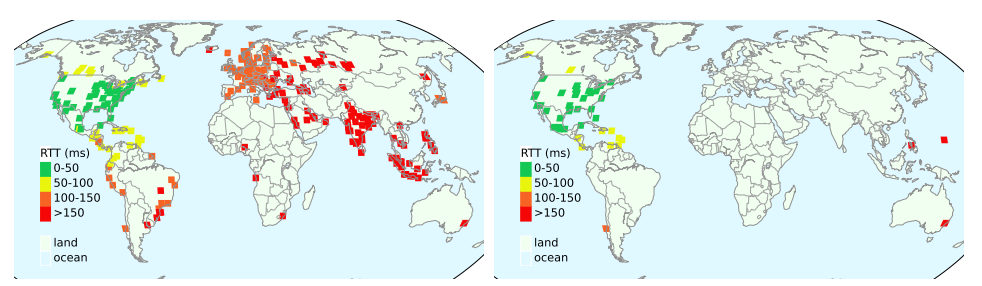
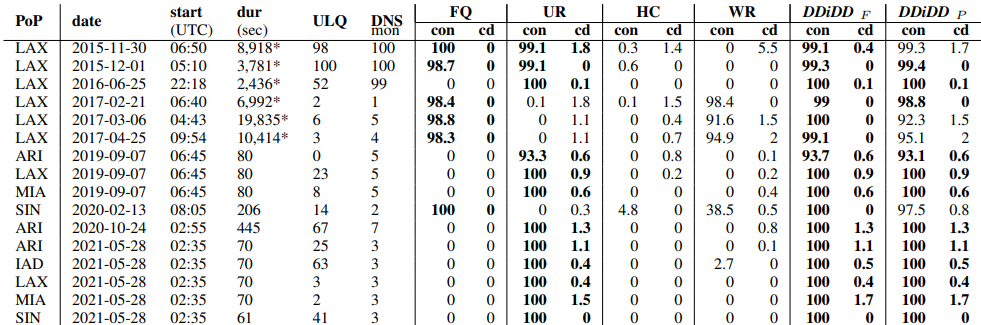
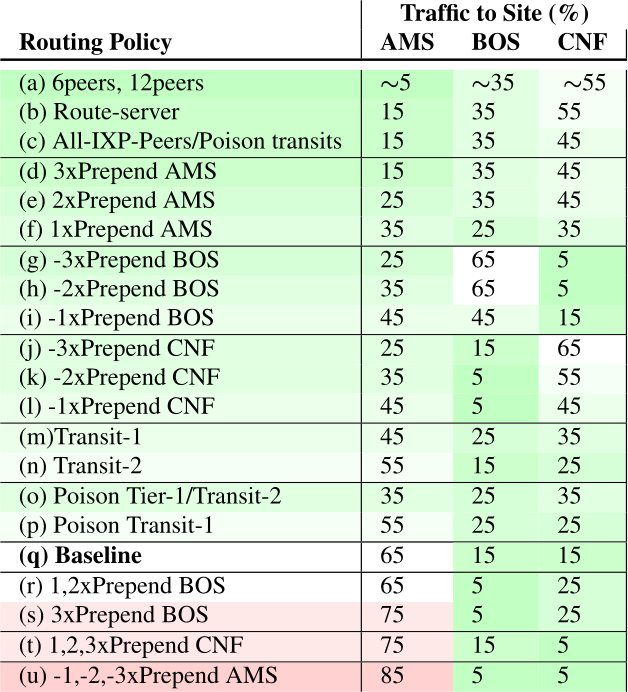
IP anycast is a commonly used method to associate users with services provided across multiple sites, and if properly used, it can provide efficient access with low latency. However, prior work has shown that polarization can occur in global anycast services, where some users of that service are routed to an anycast site on another continent, adding 100 ms or more latency compared to a nearby site. This paper describes the causes of polarization in real-world anycast and shows how to observe polarization in third-party anycast services. We use these methods to look for polarization and its causes in 7986 known anycast prefixes. We find that polarization occurs in more than a quarter of anycast prefixes, and identify incomplete connectivity to Tier-1 transit providers and route leakage by regional ISPs as common problems. Finally, working with a commercial CDN, we show how small routing changes can often address polarization, improving latency for 40% of clients, by up to 54%.
This paper is a joint work by ASM Rizvi from USC/ISI and Akamai Technologies, Tingshan Huang from Akamai Technologies, Rasit Esrefoglu from Akamai Technologies, and John Heidemann from USC/ISI. ASM Rizvi and John Heidemann’s work was partially supported by DARPA under Contract No. HR001120C0157. John Heidemann’s work was also partially supported by the NFS projects CNS-2319409, CRI-8115780, and CNS-1925737. ASM Rizvi’s work was begun while on an internship at Akamai.