I would like to congratulate Dr. Guillermo Baltra for defending his PhD at the University of Southern California in August 2023 and completing his doctoral dissertation “Improving network reliability using a formal definition of the Internet core”.

From the abstract:
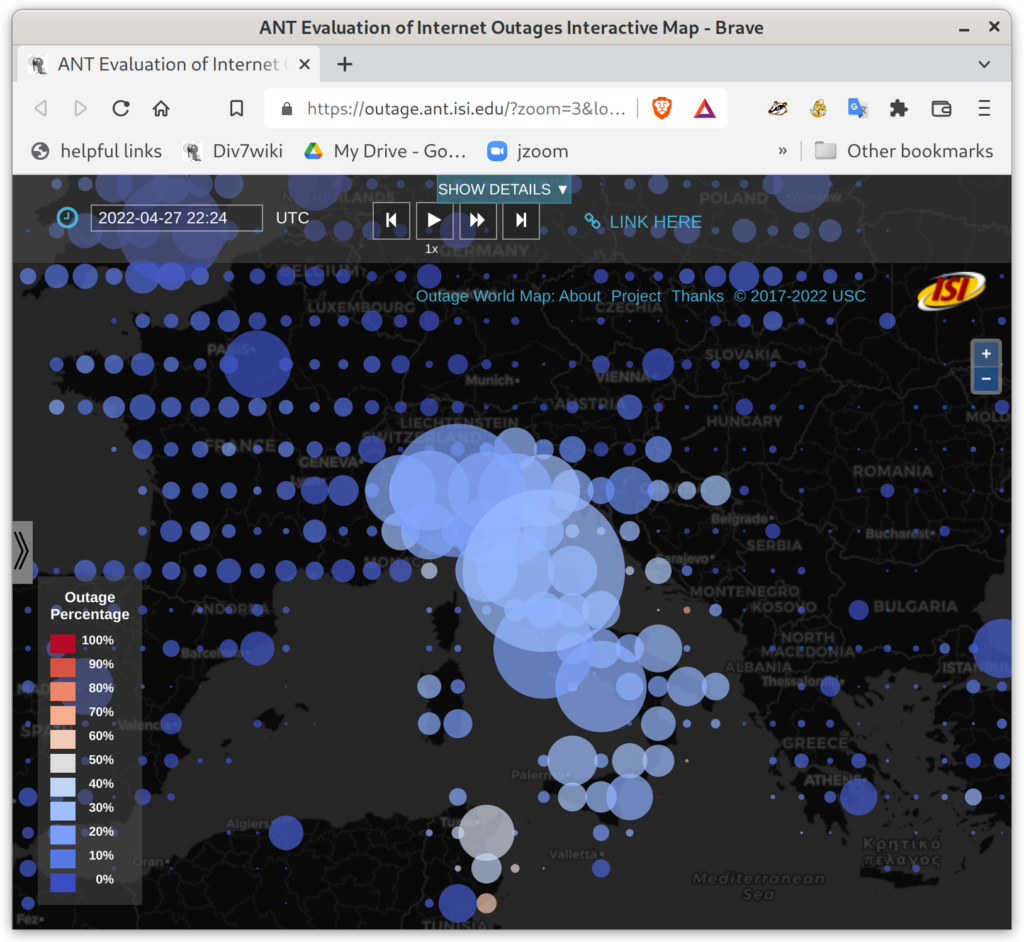
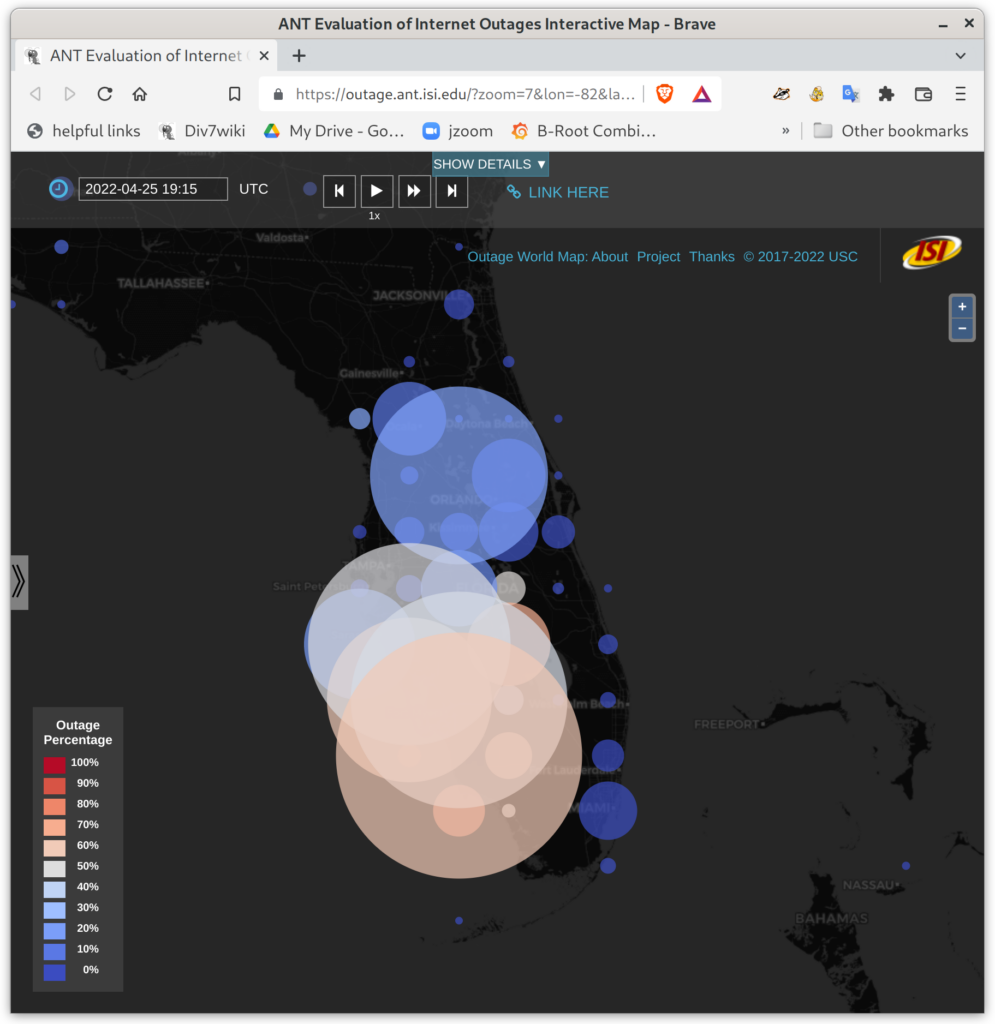
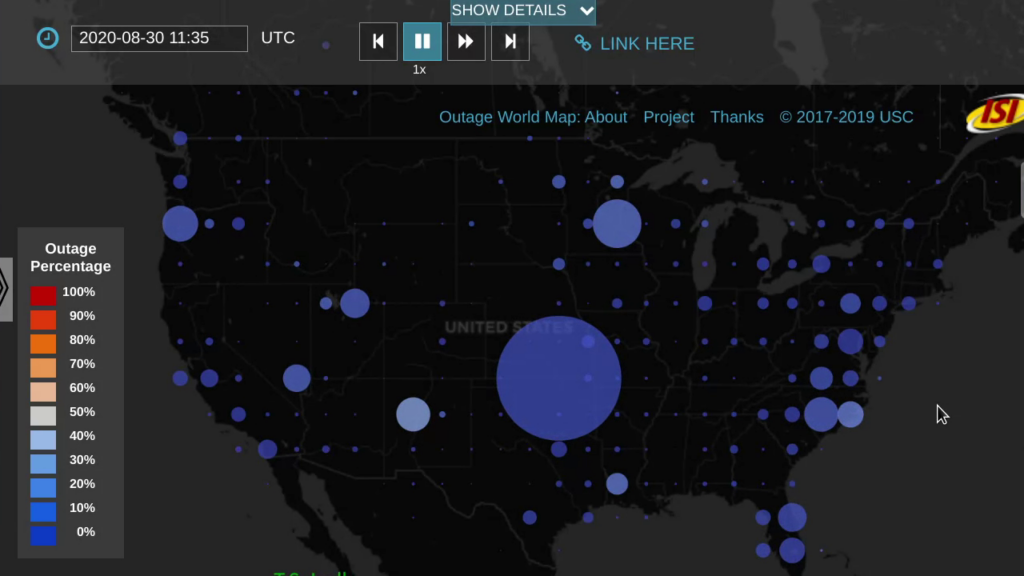
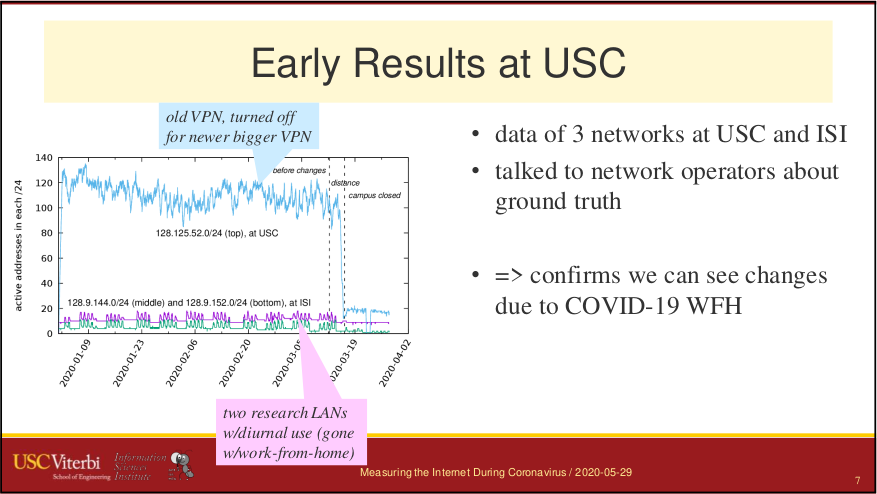
After 50 years, the Internet is still defined as “a collection of interconnected networks”. Yet seamless, universal connectivity is challenged in several ways. Political pressure threatens fragmentation due to de-peering; architectural changes such as carrier-grade NAT, the cloud makes connectivity indirect; firewalls impede connectivity; and operational problems and commercial disputes all challenge the idea of a single set of “interconnected networks”. We propose that a new, conceptual definition of the Internet core helps disambiguate questions in analysis of network reliability and address space usage.
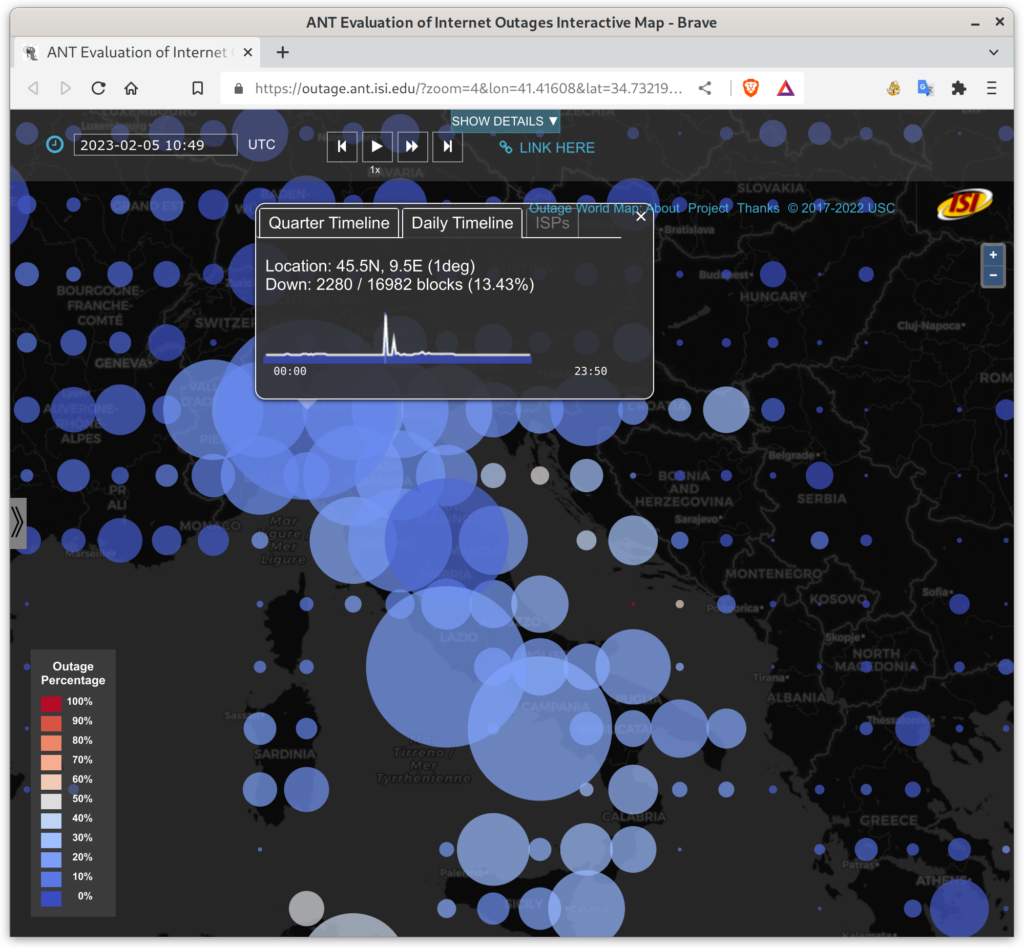
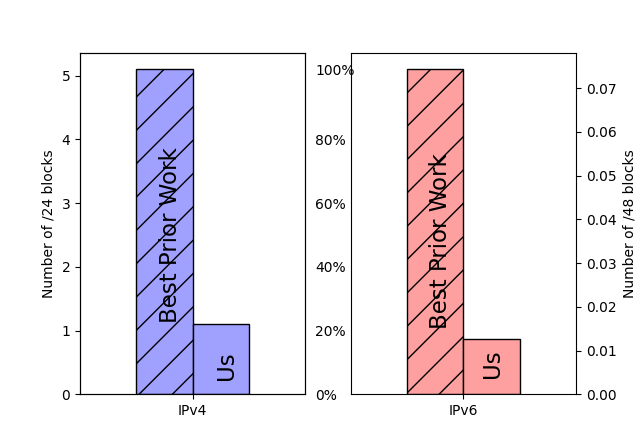
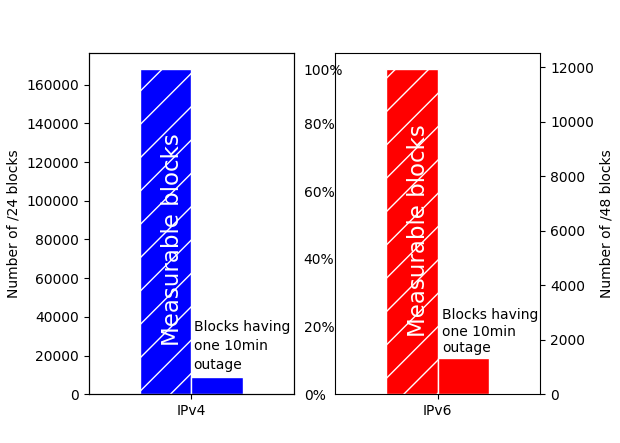
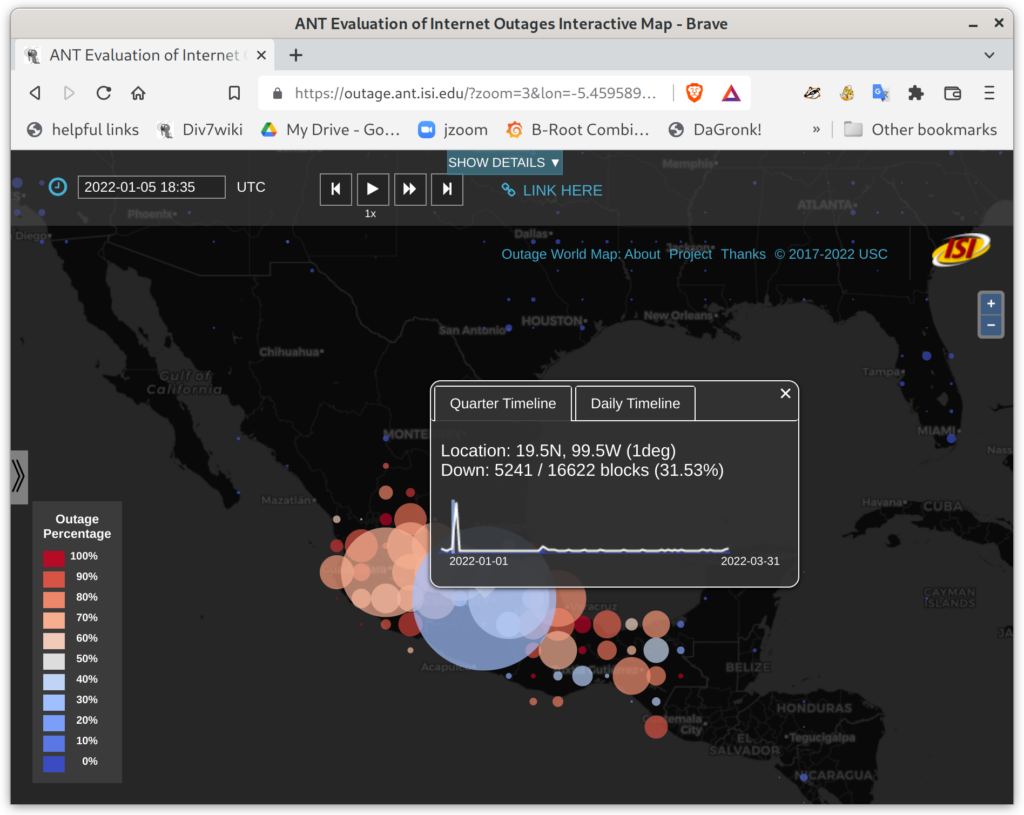
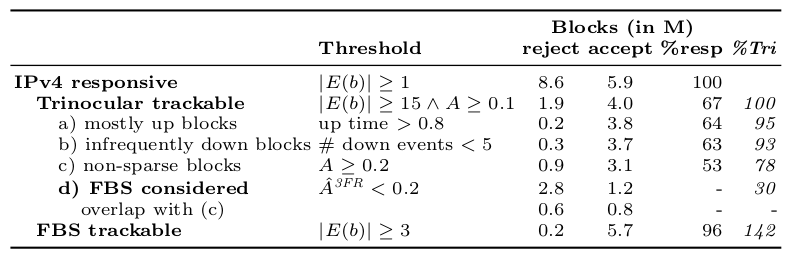
We prove this statement through three studies. First, we improve coverage of outage detection by dealing with sparse sections of the Internet, increasing from a nominal 67% responsive /24 blocks coverage to 96% of the responsive Internet. Second, we provide a new definition of the Internet core, and use it to resolve partial reachability ambiguities. We show that the Internet today has peninsulas of persistent, partial connectivity, and that some outages cause islands where the Internet at the site is up, but partitioned from the main Internet. Finally, we use our definition to identify ISP trends, with applications to policy and improving outage detection accuracy. We show how these studies together thoroughly prove our thesis statement. We provide a new conceptual definition of “the Internet core” in our second study about partial reachability. We use our definition in our first and second studies to disambiguate questions about network reliability and in our third study, to ISP address space usage dynamics.
Guillermo’s PhD work was supported by NSF grants CNS-1806785, CNS-2007106 and NSF-2028279 and DH S&T Cyber Security Division contract 70RSAT18CB0000014 and a DHS contract administred by AFRL as contract FA8750-18-2-0280, to USC Viterbi, the Armada de Chile, and the Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo de Chile (ANID).
Please see his individual publications for what data is available from his research; his results are also in use in ongoing Trinocular outage detection datasets.