The paper “Anycast vs. DDoS: Evaluating the November 2015 Root DNS Event” will appear at ACM Internet Measurement Conference in November 2016 in Santa Monica, California, USA. (previously available at http://www.isi.edu/~weilan/PAPER/IMC2016camera.pdf)
From the abstract:
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks continue to be a major threat in the Internet today. DDoS attacks overwhelm target services with requests or other traffic, causing requests from legitimate users to be shut out. A common defense against DDoS is to replicate the service in multiple physical locations or sites. If all sites announce a common IP address, BGP will associate users around the Internet with a nearby site,defining the catchment of that site. Anycast addresses DDoS both by increasing capacity to the aggregate of many sites, and allowing each catchment to contain attack traffic leaving other sites unaffected. IP anycast is widely used for commercial CDNs and essential infrastructure such as DNS, but there is little evaluation of anycast under stress. This paper provides the first evaluation of several anycast services under stress with public data. Our subject is the Internet’s Root Domain Name Service, made up of 13 independently designed services (“letters”, 11 with IP anycast) running at more than 500 sites. Many of these services were stressed by sustained traffic at 100 times normal load on Nov.30 and Dec.1, 2015. We use public data for most of our analysis to examine how different services respond to the these events. We see how different anycast deployments respond to stress, and identify two policies: sites may absorb attack traffic, containing the damage but reducing service to some users, or they may withdraw routes to shift both good and bad traffic to other sites. We study how these deployments policies result in different levels of service to different users. We also show evidence of collateral damage on other services located near the attacks.
This IMC paper is joint work of Giovane C. M. Moura, Moritz Müller, Cristian Hesselman (SIDN Labs), Ricardo de O. Schmidt, Wouter B. de Vries (U. Twente), John Heidemann, Lan Wei (USC/ISI). Datasets in this paper are derived from RIPE Atlas and are available at http://traces.simpleweb.org/ and at https://ant.isi.edu/datasets/anycast/.
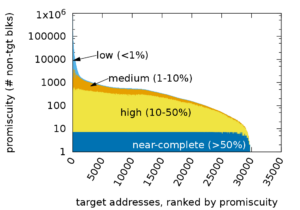
![[Moura16a] Figure 3](https://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/plot-letter-reachability-mp-scaledA-280x300.png)
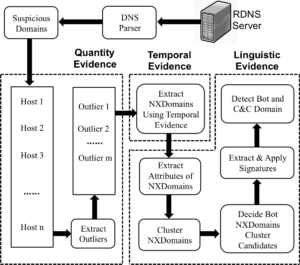
 These limitations make it very hard to detect individual bots when using traffic collected from a single network. In this paper, we introduce BotDigger, a system that detects DGA-based bots using DNS traffic without a priori knowledge of the domain generation algorithm. BotDigger utilizes a chain of evidence, including quantity, temporal and linguistic evidence
These limitations make it very hard to detect individual bots when using traffic collected from a single network. In this paper, we introduce BotDigger, a system that detects DGA-based bots using DNS traffic without a priori knowledge of the domain generation algorithm. BotDigger utilizes a chain of evidence, including quantity, temporal and linguistic evidence
![How newtork activity generates DNS backscatter that is visible at authority servers. (Figure 1 from [Fukuda15a]).](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Fukuda15a_icon-300x190.png)