The paper “Assessing Affinity Between Users and CDN Sites” (previously available at http://www.isi.edu/~xunfan/research/Fan15a.pdf) will appear at the Traffic Monitoring and Analysis Workshop in April 2015 in Barcelona, Spain.
From the abstract:
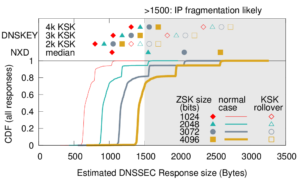
Large web services employ CDNs to improve user performance. CDNs improve performance by serving users from nearby FrontEnd (FE) Clusters. They also spread users across FE Clusters when one is overloaded or unavailable and others have unused capacity. Our paper is the first to study the dynamics of the user-to-FE Cluster mapping for Google and Akamai from a large range of client prefixes. We measure how 32,000 prefixes associate with FE Clusters in their CDNs every 15 minutes for more than a month. We study geographic and latency effects of mapping changes, showing that 50–70% of prefixes switch between FE Clusters that are very distant from each other (more than 1,000 km), and that these shifts sometimes (28–40% of the time) result in large latency shifts (100 ms or more). Most prefixes see large latencies only briefly, but a few (2–5%) see high latency much of the time. We also find that many prefixes are directed to several countries over the course of a month, complicating questions of jurisdiction.
Citation: Xun Fan, Ethan Katz-Bassett and John Heidemann.Assessing Affinity Between Users and CDN Sites. To appear in Traffic Monitoring and Analysis Workshop. Barcelona, Spain. April, 2015.
All data in this paper is available to researchers at no cost on request. Please see our CDN affinity dataset webpage.
This research is partially sponsored by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate, HSARPA, Cyber Security Division, BAA 11-01-RIKA and Air Force Re-search Laboratory, Information Directorate under agreement number FA8750-12-2-0344, NSF CNS-1351100, and via SPAWAR Systems Center Pacific under Contract No. N66001-13-C-3001. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Governmental purposes notwith-standing any copyright notation thereon. The views contained herein are those of the authors and
do not necessarily represent those of DHS or the U.S. Government.

![Predicting longitude from observed diurnal phase ([Quan14c], figure 14c)](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Quan14c_icon-300x175.png)