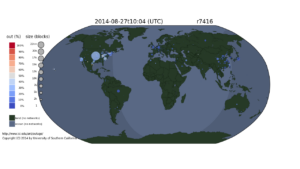
On August 27, 2014, Time Warner suffered a network outage that affected about 11 million customers for more than two hours (making national news). We have observing global network outages since December 2013, including this outage.
We recently animated this August Time Warner outage.
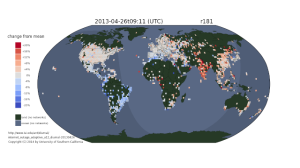
We see that the Time Warner outage lasted about two hours and affected a good swath of the United States. We caution that all large network operators have occasional outages–this animation is not intended to complain about Time Warner, but to illustrate the need to have tools that can detect and visualize national-level outages. It also puts the outage into context: we can see a few other outages in Uruguay, Brazil, and Saudi Arabia.
This analysis uses dataset usc-lander /internet_outage_adaptive_a17all-20140701, available for research use from PREDICT, or by request from us if PREDICT access is not possible.
This animation was first shown at the Dec. 2014 DHS Cyber Security Division R&D Showcase and Technical Workshop as part of the talk “Towards Understanding Internet Reliability” given by John Heidemann. This work was supported by DHS, most recently through the LACREND project.