We released a new technical report “Plumb: Efficient Processing of Multi-Users Pipelines (Extended)”, by Abdul Qadeer and John Heidemann, as ISI-TR-727. It is available at https://www.isi.edu/publications/trpublic/pdfs/isi-tr-727.pdf
From the abstract:
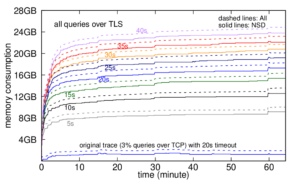
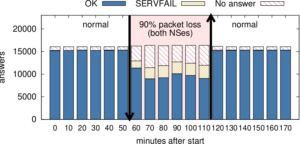
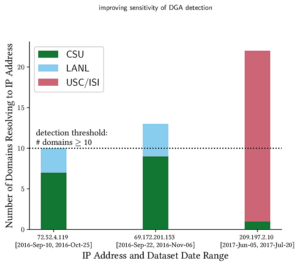
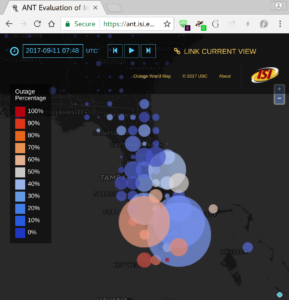
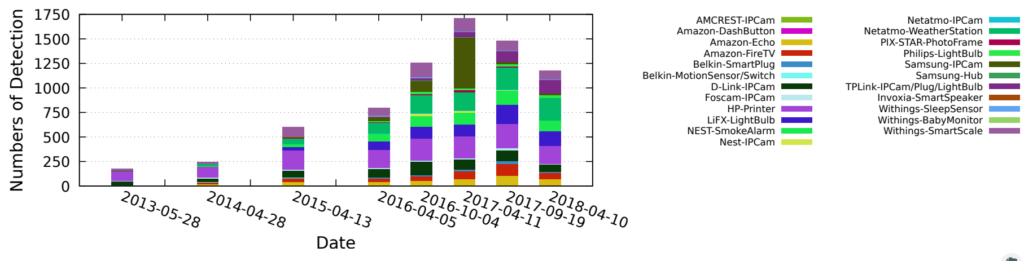
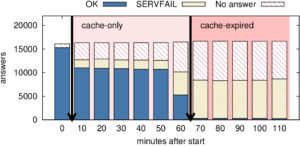
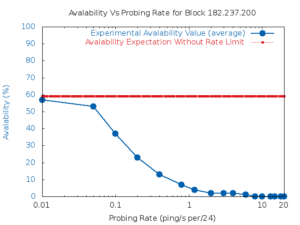
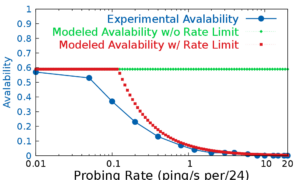
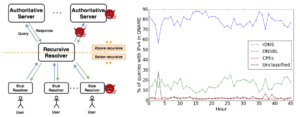
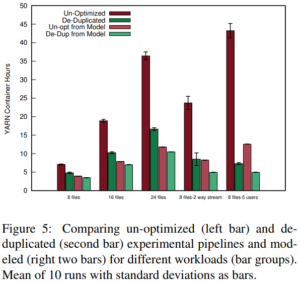
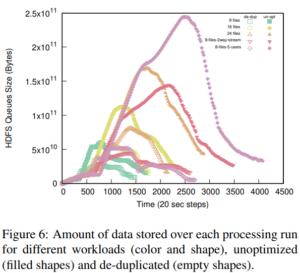
Services such as DNS and websites often produce streams of data that are consumed by analytics pipelines operated by multiple teams. Often this data is processed in large chunks (megabytes) to allow analysis of a block of time or to amortize costs. Such pipelines pose two problems: first, duplication of computation and storage may occur when parts of the pipeline are operated by different groups. Second, processing can be lumpy, with structural lumpiness occurring when different stages need different amounts of resources, and data lumpiness occurring when a block of input requires increased resources. Duplication and structural lumpiness both can result in inefficient processing. Data lumpiness can cause pipeline failure or deadlock, for example if differences in DDoS traffic compared to normal can require 6× CPU. We propose Plumb, a framework to abstract file processing for a multi-stage pipeline. Plumb integrates pipelines contributed by multiple users, detecting and eliminating duplication of computation and intermediate storage. It tracks and adjusts computation of each stage, accommodating both structural and data lumpiness. We exercise Plumb with the processing pipeline for B-Root DNS traffic, where it will replace a hand-tuned system to provide one third the original latency by utilizing 22% fewer CPU and will address limitations that occur as multiple users process data and when DDoS traffic causes huge shifts in performance.