We’re happy to welcome Greece to our browsable Internet map at http://www.isi.edu/ant/address/browse/ ! Of course Greece has always been in our Internet censuses, but George Xylomenos and George Polyzos of the Athens University of Economics and Business (their lab) helped set up a new observation site. Greece now provides a new vantage point for Internet censuses.
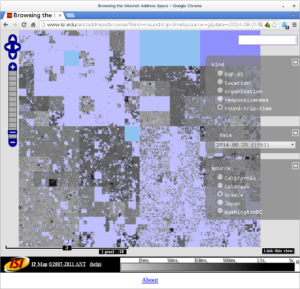
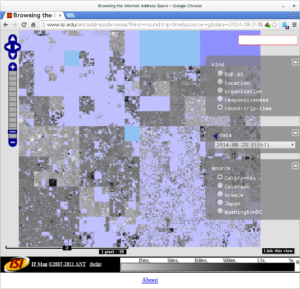
The differences in the census are small, as one would hope, since it’s a global Internet. However, when we look at latency (the time it takes for an IP address to reply to our requests), Greece gives us a European view.
Compare the lower-left corner of the Internet, since that is European IPv4 address space:
In addition to big thanks to George Xylomenos and George Polyzos of AUEB (σας ευχαριστώ!) and AUEB for institutional funding for this work. We also thank Christos Papadopoulos (Colorado State) for helping with many details, and Colin Perkins (U. Glasgow) for discussions about potential European hosts.
Data from our Greece census is available to researchers at no cost on the same terms as our existing census data. See our datasets page for details. Greek data starts with it61 as of 2014-08-29.