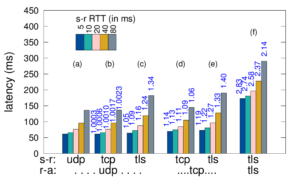
We have released a new technical report “Anycast Latency: How Many Sites Are Enough?”, ISI-TR-2016-708, available at http://www.isi.edu/%7ejohnh/PAPERS/Schmidt16a.pdf.
![[Schmidt16a] figure 4: distribution of measured latency (solid lines) to optimal possible latency (dashed lines) for 4 Root DNS anycast deployments.](https://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/plot-cdf-optimal-300x210.png)
Anycast is widely used today to provide important services including naming and content, with DNS and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). An anycast service uses multiple sites to provide high availability, capacity and redundancy, with BGP routing associating users to nearby anycast sites. Routing defines the catchment of the users that each site serves. Although prior work has studied how users associate with anycast services informally, in this paper we examine the key question how many anycast sites are needed to provide good latency, and the worst case latencies that specific deployments see. To answer this question, we must first define the optimal performance that is possible, then explore how routing, specific anycast policies, and site location affect performance. We develop a new method capable of determining optimal performance and use it to study four real-world anycast services operated by different organizations: C-, F-, K-, and L-Root, each part of the Root DNS service. We measure their performance from more than worldwide vantage points (VPs) in RIPE Atlas. (Given the VPs uneven geographic distribution, we evaluate and control for potential bias.) Key results of our study are to show that a few sites can provide performance nearly as good as many, and that geographic location and good connectivity have a far stronger effect on latency than having many nodes. We show how often users see the closest anycast site, and how strongly routing policy affects site selection.
This technical report is joint work of Ricardo de O. Schmidt and Jan Harm Kuipers (U. Twente) and John Heidemann (USC/ISI). Datasets in this paper are derived from RIPE Atlas and are available at http://traces.simpleweb.org/.
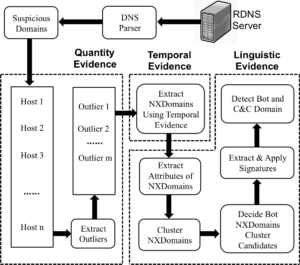
 These limitations make it very hard to detect individual bots when using traffic collected from a single network. In this paper, we introduce BotDigger, a system that detects DGA-based bots using DNS traffic without a priori knowledge of the domain generation algorithm. BotDigger utilizes a chain of evidence, including quantity, temporal and linguistic evidence
These limitations make it very hard to detect individual bots when using traffic collected from a single network. In this paper, we introduce BotDigger, a system that detects DGA-based bots using DNS traffic without a priori knowledge of the domain generation algorithm. BotDigger utilizes a chain of evidence, including quantity, temporal and linguistic evidence
![How newtork activity generates DNS backscatter that is visible at authority servers. (Figure 1 from [Fukuda15a]).](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/Fukuda15a_icon-300x190.png)