The paper “A Look at Router Geolocation in Public and Commercial Databases” has appeared in the 2017 Internet Measurement Conference (IMC) on November 1-3, 2017 in London, United Kingdom.
From the abstract:
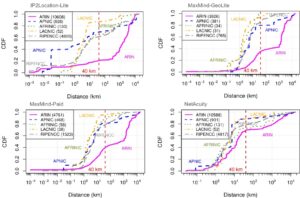
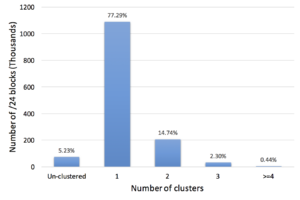
Internet measurement research frequently needs to map infrastructure components, such as routers, to their physical locations. Although public and commercial geolocation services are often used for this purpose, their accuracy when applied to network infrastructure has not been sufficiently assessed. Prior work focused on evaluating the overall accuracy of geolocation databases, which is dominated by their performance on end-user IP addresses. In this work, we evaluate the reliability of router geolocation in databases. We use a dataset of about 1.64M router interface IP addresses extracted from the CAIDA Ark dataset to examine the country- and city-level coverage and consistency of popular public and commercial geolocation databases. We also create and provide a ground-truth dataset of 16,586 router interface IP addresses and their city-level locations, and use it to evaluate the databases’ accuracy with a regional breakdown analysis. Our results show that the databases are not reliable for geolocating routers and that there is room to improve their country- and city-level accuracy. Based on our results, we present a set of recommendations to researchers concerning the use of geolocation databases to geolocate routers.
The work in this paper was joint work by Manaf Gharaibeh, Anant Shah, Han Zhang, Christos Papadopoulos (Colorado State University), Brad Huffaker (CAIDA / UC San Diego), and Roya Ensafi (University of Michigan). The findings of this work are highlighted in an APNIC blog post “Should we trust the geolocation databases to geolocate routers?”. The ground truth datasets used in the paper are available via IMPACT.