The paper “Connection-Oriented DNS to Improve Privacy and Security” will appear at the 36th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy in May 2015 in San Jose, CA, USA (previously available at http://www.isi.edu/~liangzhu/papers/Zhu15b.pdf)
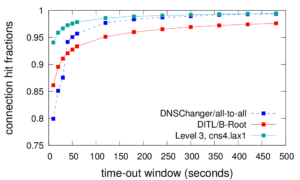
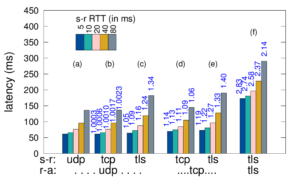
The Domain Name System (DNS) seems ideal for connectionless UDP, yet this choice results in challenges of eavesdropping that compromises privacy, source-address spoofing that simplifies denial-of-service (DoS) attacks on the server and third parties, injection attacks that exploit fragmentation, and reply-size limits that constrain key sizes and policy choices. We propose T-DNS to address these problems. It uses TCP to smoothly support large payloads and to mitigate spoofing and amplification for DoS. T-DNS uses transport-layer security (TLS) to provide privacy from users to their DNS resolvers and optionally to authoritative servers. TCP and TLS are hardly novel, and expectations about DNS suggest connections will balloon client latency and overwhelm server with state. Our contribution is to show that T-DNS significantly improves security and privacy: TCP prevents denial-of-service (DoS) amplification against others, reduces the effects of DoS on the server, and simplifies policy choices about key size. TLS protects against eavesdroppers to the recursive resolver. Our second contribution is to show that with careful implementation choices, these benefits come at only modest cost: end-to-end latency from TLS to the recursive resolver is only about 9% slower when UDP is used to the authoritative server, and 22% slower with TCP to the authoritative. With diverse traces we show that connection reuse can be frequent (60–95% for stub and recursive resolvers, although half that for authoritative servers), and after connection establishment, experiments show that TCP and TLS latency is equivalent to UDP. With conservative timeouts (20 s at authoritative servers and 60 s elsewhere) and estimated per-connection memory, we show that server memory requirements match current hardware: a large recursive resolver may have 24k active connections requiring about 3.6 GB additional RAM. Good performance requires key design and implementation decisions we identify: query pipelining, out-of-order responses, TCP fast-open and TLS connection resumption, and plausible timeouts.
The work in the paper is by Liang Zhu, Zi Hu and John Heidemann (USC/ISI), Duane Wessels and Allison Mankin (both of Verisign Labs), and Nikita Somaiya (USC/ISI). Earlier versions of this paper were released as ISI-TR-688 and ISI-TR-693; this paper adds results and supercedes that work.
The data in this paper is available to researchers at no cost on request. Please see T-DNS-experiments-20140324 at dataset page.

![Predicting longitude from observed diurnal phase ([Quan14c], figure 14c)](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Quan14c_icon-300x175.png)
![Comparing observed diurnal phase and geolocation longitude for 287k geolocatable, diurnal blocks ([Quan14b], figure 14b)](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/Quan14b_icon-300x210.png)