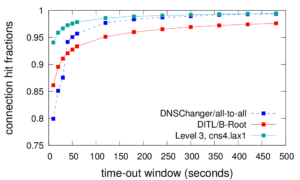
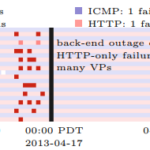
The paper “Privacy Principles for Sharing Cyber Security Data” (available at https://www.isi.edu/~calvin/papers/Fisk15a.pdf) will appear at the International Workshop on Privacy Engineering (co-located with IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy) on May 21, 2015 in San Jose, California.
From the abstract:
Sharing cyber security data across organizational boundaries brings both privacy risks in the exposure of personal information and data, and organizational risk in disclosing internal information. These risks occur as information leaks in network traffic or logs, and also in queries made across organizations. They are also complicated by the trade-offs in privacy preservation and utility present in anonymization to manage disclosure. In this paper, we define three principles that guide sharing security information across organizations: Least Disclosure, Qualitative Evaluation, and Forward Progress. We then discuss engineering approaches that apply these principles to a distributed security system. Application of these principles can reduce the risk of data exposure and help manage trust requirements for data sharing, helping to meet our goal of balancing privacy, organizational risk, and the ability to better respond to security with shared information.
The work in the paper is by Gina Fisk (LANL), Calvin Ardi (USC/ISI), Neale Pickett (LANL), John Heidemann (USC/ISI), Mike Fisk (LANL), and Christos Papadopoulos (Colorado State). This work is supported by DHS S&T, Cyber Security division.
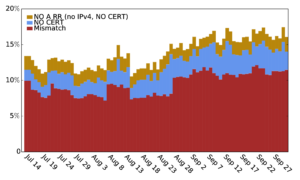
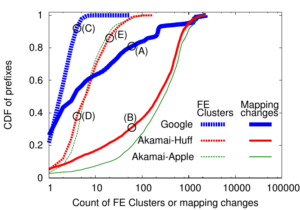 Large web services employ CDNs to improve user performance. CDNs improve performance by serving users from nearby FrontEnd (FE) Clusters. They also spread users across FE Clusters when one is overloaded or unavailable and others have unused capacity. Our paper is the first to study the dynamics of the user-to-FE Cluster mapping for Google and Akamai from a large range of client prefixes. We measure how 32,000 prefixes associate with FE Clusters in their CDNs every 15 minutes for more than a month. We study geographic and latency effects of mapping changes, showing that 50–70% of prefixes switch between FE Clusters that are very distant from each other (more than 1,000 km), and that these shifts sometimes (28–40% of the time) result in large latency shifts (100 ms or more). Most prefixes see large latencies only briefly, but a few (2–5%) see high latency much of the time. We also find that many prefixes are directed to several countries over the course of a month, complicating questions of jurisdiction.
Large web services employ CDNs to improve user performance. CDNs improve performance by serving users from nearby FrontEnd (FE) Clusters. They also spread users across FE Clusters when one is overloaded or unavailable and others have unused capacity. Our paper is the first to study the dynamics of the user-to-FE Cluster mapping for Google and Akamai from a large range of client prefixes. We measure how 32,000 prefixes associate with FE Clusters in their CDNs every 15 minutes for more than a month. We study geographic and latency effects of mapping changes, showing that 50–70% of prefixes switch between FE Clusters that are very distant from each other (more than 1,000 km), and that these shifts sometimes (28–40% of the time) result in large latency shifts (100 ms or more). Most prefixes see large latencies only briefly, but a few (2–5%) see high latency much of the time. We also find that many prefixes are directed to several countries over the course of a month, complicating questions of jurisdiction.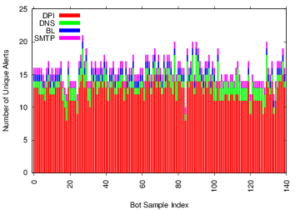
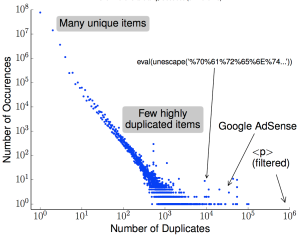
![Predicting longitude from observed diurnal phase ([Quan14c], figure 14c)](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Quan14c_icon-300x175.png)
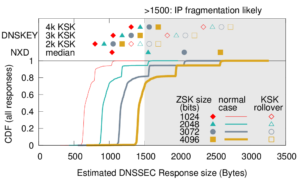
![Comparing observed diurnal phase and geolocation longitude for 287k geolocatable, diurnal blocks ([Quan14b], figure 14b)](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/Quan14b_icon-300x210.png)