We’re happy to announce that our browsable Internet map at http://www.isi.edu/ant/address/browse/ now includes IP geolocation.
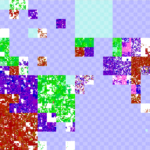
We plot the latitude and longitude of each IP address around the world as a specific color, placing them on our IPv4 map (the zoomable Hilbert curve). Thus we can show how blocks of IPv4 addresses map (above) to the globe (below).


On the IP map, we show latitude/longitude by color. For each address, the longitude is the hue (the colors around the rainbow), so North America is blue; South America, fuschia; Europe and Africa, red; and Asia to Australia yellow to green. The latitude controls lightness, so things north of the equator are darker, while those south of the equator are lighter. Thus Japan is dark green, while Australia is teal, and Scandanavia is dark read, while south Africa is orange. (We have released the source code to do this mapping with a BSD license.)
The IP map shows IP all 4 billion addresses on the Hilbert curve. We have discussed this mapping before (see our poster).
Our IP map is zoomable and draggable, so one can look at particular regions of interest. For example, here is 128/8, including ISI (in Los Angeles, dark blue), between UC San Diego (also dark blue) and University of Maryland (US east coast, so purple), while the Fininnish University of Helsinki is dark brown, and the Australian University of Melboure is lime green.

Our geolocation data comes from three sources:
All of these geolocation sources have varying levels of accuracy, however we hope that the ability to visually relate IP addresses (onthe Hilbert curve) with geolocation (via latitude and longitude as shownby color) provides a fresh look at IP addresses and their locations.
This geolocation work is due to Zi Hu, Yuri Pradkin, and John Heideman. This work and visualization has been supported by the AMITE project through DHS, and the data (both processed geolocation results and raw data if you can improve our accuracy) will be available through the LANDER project’s datasets and the PREDICT program.