John Heidemann gave the talk “New Opportunities for Research and Experiments in Internet Naming And Identification” at the AIMS 2016 workshop at CAIDA, La Jolla, California on February 11, 2016. Slides are available at http://www.isi.edu/~johnh/PAPERS/Heidemann16a.pdf.

From the abstract:
DNS is central to Internet use today, yet research on DNS today is challenging: many researchers find it challenging to create realistic experiments at scale and representative of the large installed base, and datasets are often short (two days or less) or otherwise limited. Yes DNS evolution presses on: improvements to privacy are needed, and extensions like DANE provide an opportunity for DNS to improve security and support identity management. We exploring how to grow the research community and enable meaningful work on Internet naming. In this talk we will propose new research infrastructure to support to realistic DNS experiments and longitudinal data studies. We are looking for feedback on our proposed approaches and input about your pressing research problems in Internet naming and identification.
For more information see our project website.
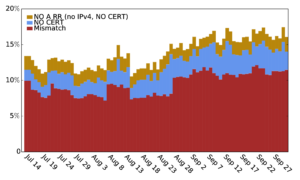
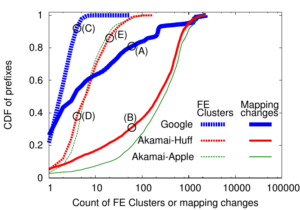 Large web services employ CDNs to improve user performance. CDNs improve performance by serving users from nearby FrontEnd (FE) Clusters. They also spread users across FE Clusters when one is overloaded or unavailable and others have unused capacity. Our paper is the first to study the dynamics of the user-to-FE Cluster mapping for Google and Akamai from a large range of client prefixes. We measure how 32,000 prefixes associate with FE Clusters in their CDNs every 15 minutes for more than a month. We study geographic and latency effects of mapping changes, showing that 50–70% of prefixes switch between FE Clusters that are very distant from each other (more than 1,000 km), and that these shifts sometimes (28–40% of the time) result in large latency shifts (100 ms or more). Most prefixes see large latencies only briefly, but a few (2–5%) see high latency much of the time. We also find that many prefixes are directed to several countries over the course of a month, complicating questions of jurisdiction.
Large web services employ CDNs to improve user performance. CDNs improve performance by serving users from nearby FrontEnd (FE) Clusters. They also spread users across FE Clusters when one is overloaded or unavailable and others have unused capacity. Our paper is the first to study the dynamics of the user-to-FE Cluster mapping for Google and Akamai from a large range of client prefixes. We measure how 32,000 prefixes associate with FE Clusters in their CDNs every 15 minutes for more than a month. We study geographic and latency effects of mapping changes, showing that 50–70% of prefixes switch between FE Clusters that are very distant from each other (more than 1,000 km), and that these shifts sometimes (28–40% of the time) result in large latency shifts (100 ms or more). Most prefixes see large latencies only briefly, but a few (2–5%) see high latency much of the time. We also find that many prefixes are directed to several countries over the course of a month, complicating questions of jurisdiction.