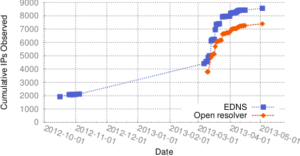
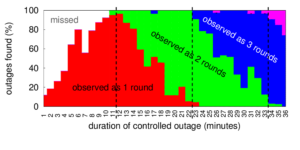
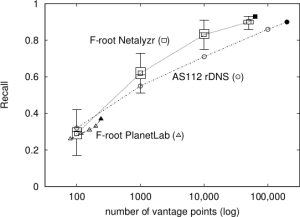
We released a new technical report “T-DNS: Connection-Oriented DNS to Improve Privacy and Security”, ISI-TR-2014-688, available as http://www.isi.edu/~johnh/PAPERS/Zhu14a.pdf
From the abstract: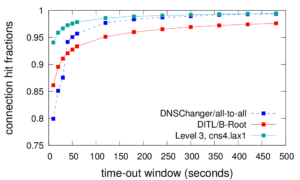
This paper explores connection-oriented DNS to improve DNS security and privacy. DNS is the canonical example of a connectionless, single packet, request/response protocol, with UDP as its dominant transport. Yet DNS today is challenged by eavesdropping that compromises privacy, source-address spoofing that results in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks on the server and third parties, injection attacks that exploit fragmentation, and size limitations that constrain policy and operational choices. We propose t-DNS to address these problems: it combines TCP to smoothly support large payloads and mitigate spoofing and amplification for DoS. T-DNS uses transport-layer security (TLS) to provide privacy from users to their DNS resolvers and optionally to authoritative servers. Traditional wisdom is that connection setup will balloon latency for clients and overwhelm servers. These are myths—our model of end-to-end latency shows TLS to the recursive resolver is only about 21% slower, with UDP to the authoritative server. End-to-end latency is 90% slower with TLS to recursive and TCP to authoritative. Experiments behind these models show that after connection establishment, TCP and TLS latency is equivalent to UDP. Using diverse trace data we show that frequent connection reuse is possible (60–95% for stub and recursive resolvers, although half that for authoritative servers). With conservative timeouts (20 s at authoritative servers and 60 s elsewhere) we show that server memory requirements match current hardware: a large recursive resolver may have 25k active connections consuming about 9 GB of RAM. We identify the key design and implementation decisions needed to minimize overhead—query pipelining, out-of-order responses, TLS connection resumption, and plausible timeouts.
![Estimated impact on user QoE in four cable cut incidents (Figure 13 from [Cai13c])](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/qoe_play_time_350k_vod_3d_all-300x200.png)
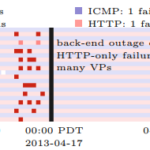
![[Calder13a] figure 5a](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Calder13a_icon-300x156.png)