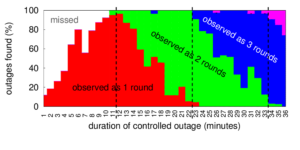
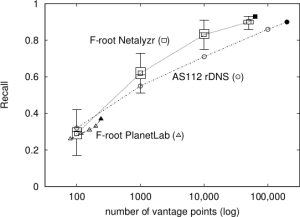
The paper “Replay of Malicious Traffic in Network Testbeds” (by Alefiya Hussain, Yuri Pradkin, and John Heidemann) will appear in the 3th IEEE Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST) in Waltham, Mass. in Nov. 2013. The paper is available at http://www.isi.edu/~johnh/PAPERS/Hussain13a.
In this paper we present tools and methods to integrate attack measurements from the Internet with controlled experimentation on a network testbed. We show that this approach provides greater fidelity than synthetic models. We compare the statistical properties of real-world attacks with synthetically generated constant bit rate attacks on the testbed. Our results indicate that trace replay provides fine time-scale details that may be absent in constant bit rate attacks. Additionally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach to study new and emerging attacks. We replay an Internet attack captured by the LANDER system on the DETERLab testbed within two hours.
Data from the paper is available as DoS_DNS_amplification-20130617 from the authors or http://www.predict.org, and the tools are at deterlab).
![Visualization of low-rate periodicity, before and after installation of a keylogger. [Bartlett11a, figure 3]](http://ant.isi.edu/blog/wp-content/uploads/2011/04/Bartlett11a_icon-227x300.png)