Our new paper “Ebb and Flow: Implications of ISP Address Dynamics” will appear at the 2024 Conference on Passive and Active Measurements (PAM 2024).
From the abstract:
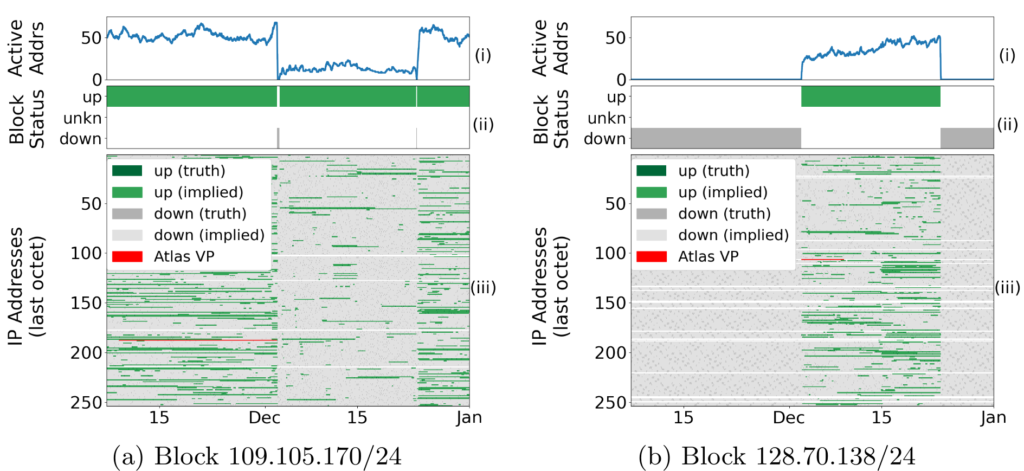
Address dynamics are changes in IP address occupation as users come and go, ISPs renumber them for privacy or for routing maintenance. Address dynamics affect address reputation services, IP geolocation, network measurement, and outage detection, with implications of Internet governance, e-commerce, and science. While prior work has identified diurnal trends in address use, we show the effectiveness of Multi-Seasonal-Trend using Loess decomposition to identify both daily and weekly trends. We use ISP-wide dynamics to develop IAS, a new algorithm that is the first to automatically detect ISP maintenance events that move users in the address space. We show that 20% of such events result in /24 IPv4 address blocks that become unused for days or more, and correcting nearly 41k false outages per quarter. Our analysis provides a new understanding about ISP address use: while only about 2.8% of ASes (1,730) are diurnal, some diurnal ASes show more than 20% changes each day. It also shows greater fragmentation in IPv4 address use compared to IPv6.
This paper is a joint work of Guillermo Baltra, Xiao Song, and John Heidemann. Datasets from this paper can be found at https://ant.isi.edu/datasets/outage. This work was supported by NSF (MINCEQ, NSF 2028279; EIEIO CNS-2007106.